Clinical Quick Reference Guides / Medical Terminology Companion Guide
Expanded Medical Terminology Guide To Accompany PrismRA Review
Getting to know these terms will help reinforce the study guide materials.
Medical Terminology
Study Tip: Take notes and add key points and action items in the side column of your notebook (Sticky Tabs Transparent Style are great for reminders!)
Angiogenesis - blood vessel formation in which new vessels emerge from existing vessels
Arthropathy - any disease of the joints
Arthroplasty - joint replacement
Autoantibodies - antibodies produced by the immune system directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins
ACPAs (Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies) - autoantibodies that are directed against peptides and proteins that are citrullinated; present in a majority of patients with RA
DMARDs - disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; medicines that are considered the gold standard for RA treatment; that can slow the progression of the disease; helping prevent severe joint damage; and other complications
Histopathologic – the microscopic examination of tissue
HLA genes - human leukocyte antigen genes; research indicates these genes significantly increase the risk of developing RA - other genes also appear to be linked to increased susceptibility, including: STAT4, PTPN22, TRAF1-C5, PADI4, CTLA4
Joint fusion - surgical joint removal; the two ends of bones are “fused” together.
Nodule biopsy - this diagnostic exam involves taking a small tissue to be studied under a microscope; the procedure checks for cancer/ abnormal cells
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) – systemic autoimmune disease; leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues
RF (Rheumatoid factor) - autoantibody; can be helpful in RA diagnosis, however, RF is not specific to RA, and there are many factors that can impact RF lab results
Rheumatoid nodules - most common dermatologic manifestation of RA; they are firm lumps that appear subcutaneously near certain joints (e.g. fingers, behind the heel)
seropositive RA - patients have ACPAs (anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides) found during serum testing; these antibodies attack the synovial joints and produce symptoms
seronegative RA - patients have the condition but lack ACPAs or RF in their blood
Synovial joints (diarthroses) - joints that a freely mobile
TNF (Tumor necrosis factor) - protein capable of causing inflammation
TNFi (tumor necrosis factor inhibitor) - biologic therapies that help stop inflammation and are used worldwide to treat inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
Additional Diagnostics:
C-reactive protein (CRP) – is also a measure of inflammation. This protein is produced by the liver when there is inflammation anywhere in the body. The higher the inflammation, the greater the elevation in CRP.
Sed Rate - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) A blood test that helps indicate the amount of inflammation in a persons body by measures how fast red blood cells cling together and settle to the bottom of a tube over the course of an hour.
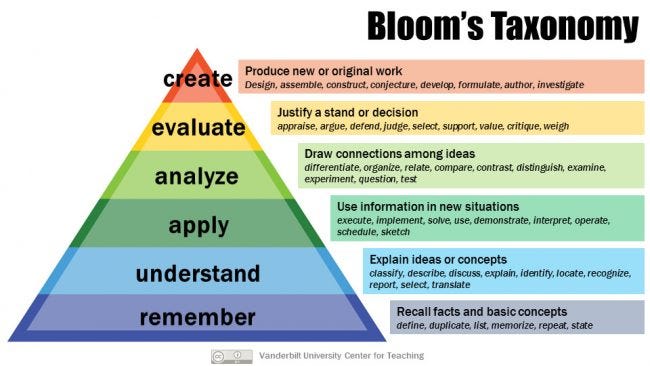
In Bloom’s taxonomy, learning begins with basic concepts. Keep this in mind as you review, remembering that each level is crucial to the development of the next. So called “basic knowledge” —(the first stage of learning) is what leads you to develop the abilities and skills required to complete the pedagogical process.
Don’t Forget To Like, Share, & Subscribe To Receive Study Guides Emailed Directly!
Clinical Quick Reference Monthly Newsletter/ November & December 2023 - New Test For RA Patients
This reference guide will review concepts related to Rheumatoid Arthritis and the PrismRA test.
Disclaimer: The above study guide represents study materials, always seek and follow the advice of your medical provider for any acute or chronic medical issues or questions.
Medical Terminology Companion Resources:
Medline.gov
CDC & NIH
NHS (Uk)
https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/blooms-taxonomy/