Clinical Quick Reference Monthly Newsletter / November 2022 / Ozempic® – A Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Agonist
Clinical Quick Reference Guides - Medication Review / Semaglutide

This review will assist the learner by introducing basics associated with semaglutide and its prescription use.
Ozempic ® is also known by the generic name semaglutide. Semaglutide is an injectable medication that is offered in strengths of 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg. This prescription drug is most commonly used with diet and exercise strategies to improve blood sugar in adult patients who have been diagnosed with T2D.
Semaglutide has additionally been found to help reduce their risk of major cardiovascular events. In T2D patients with known heart disease, this incretin mimetic medication has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
What Type of Medication is Semaglutide?
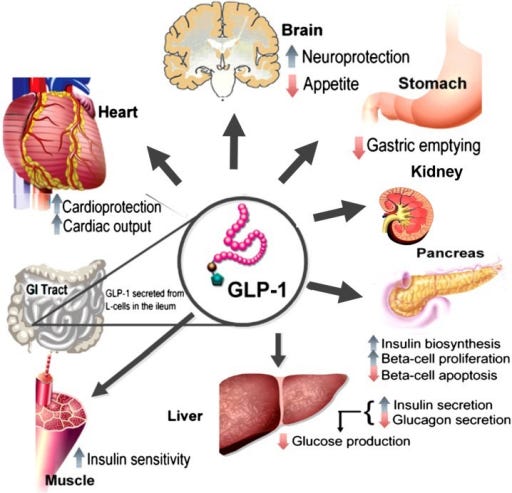
Semaglutide, or Ozempic®, is a prescription drug that is similar to a hormone that occurs naturally in the human body. This hormone helps control blood sugar, digestion and insulin levels.
Semaglutide is part of a class of medications referred to as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists (incretin mimetics).
These type of drugs work by binding to GLP-1 receptors, thereby stimulating release of insulin from the pancreas.
Other GLP-1 agonists include:
Liraglutide
Lixisenatide
When Was Ozempic® Approved?
Ozempic® was approved for type 2 diabetes by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2017.
Semaglutide Precautions
Healthcare professionals should be careful not to confuse Ozempic®, or semglutide, with insulin.
Semaglutide works to help the pancreas release insulin. This medication also helps to prevent the patient’s liver from making and releasing sugar. Semaglutide slows movement of food through the stomach, an effect which may aid in weight loss.
Semaglutide Side Effects
Providers should be aware that as with any other medication, benefits associated with semaglutide come with risks and the potential for side effects.
Healthcare professionals should provide patients with appropriate education regarding the benefits and risks.
In rare cases these medications have been associated with serious side effects.
Serious side effects associated with semaglutide/Ozempic® include:
allergic reaction
diabetic retinopathy
gallstones
hypoglycemia
increased risk of thyroid cancer
kidney issues
pancreatitis
Research indicates that semaglutide (Ozempic®) is effective at controlling blood glucose with a low risk of hypoglycemia. Patients that are overweight or obese generally lose some weight while using the drugs. On average the weight loss is about 6.5 pounds, or 3 kg. While most patients will only experience minimal side effects (health teach patients about the gastrointestinal effects of semaglutide: abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and nausea); it is crucial that healthcare providers discuss and review the potential for more serious effects.
Medical Terminology
Photo by Christin Hume on Unsplash Incretins - group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels
Insulin - a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets; regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cell
GLP-1 - a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone
T2D - form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin
Anatomy & Physiology
Reference: https://openi.nlm.nih.gov/detailedresult.phpimg=PMC4575308_13300_2015_127_Fig1_HTML&req=4
Disclaimer:
The above study guide is not intended to be used as medical advice. The above study guide represents study materials, always seek and follow the advice of your medical provider for any acute or chronic medical issues or questions.
Reference Source Material:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
NIH