CQRG 2024 Medical Terminology Bootcamp
SESSION 9 / INTRODUCTION TO THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Welcome!
If you are new to our medical terminology program we invite you to browse our previous lessons and program activities. Simply click on the PROGRAMS tab above to view individual lessons and materials. Additional activities and reviews are posted on a weekly basis in the NOTES section. Each lesson in the program is a standalone experience, so there is never a worry if you need to take a break. Subscribe to receive the lessons emailed to you, or follow along in the Notes section.
The Cardiovascular System
The primary function of the cardiovascular system is to ensure proper circulation of the blood throughout the body.
This process begins with the heart, as it delivers the impulse for all blood flow in the body. The pulmonary circulation facilitates oxygenation of blood, while the systemic circulation enables the oxygenated blood and essential nutrients to reach all parts of the body.
The cardiovascular system is also referred to as the circulatory system.
Major Anatomical Features
The circulatory system is responsible for supplying oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to muscles, tissues, and organs.
The circulatory system also removes wastes from cells and organs to be disposed of.
Major Components of the Cardiovascular System
The major components of the circulatory system are:
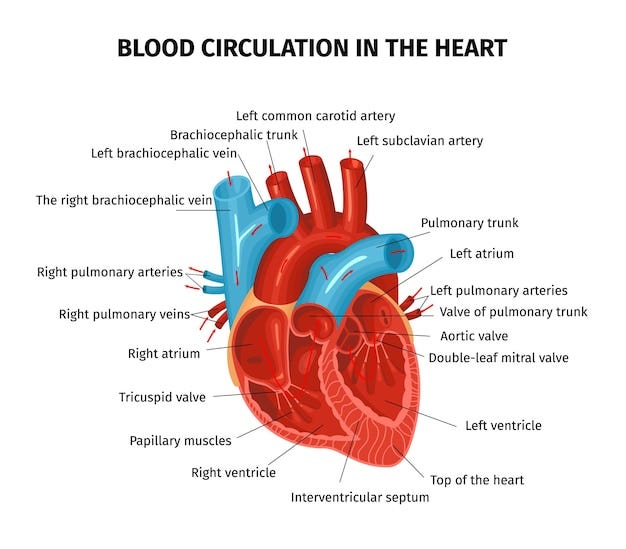
The Heart
A muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body
The Blood Vessels
These include arteries, veins and capillaries
The Blood
This is composed of red and white blood cells, plasma, and platelets
The circulatory system has three circuits through which blood flows in a continuous pattern.
Circuits
The pulmonary circuit.
This circuit transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it receives oxygen. The oxygenated blood is then returned to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
The systemic circuit.
In this circuit, oxygenated blood carrying nutrients and hormones is pumped from the heart to the body's tissues. The blood circulates through the veins, waste products are collected as the body utilizes the oxygen, nutrients, and hormones.
The coronary circuit.
This circuit specifically refers to the arteries of the heart. It supplies oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Subsequently, the coronary circuit returns oxygen-depleted blood to the right atrium of the heart to be sent to the lungs for oxygenation.
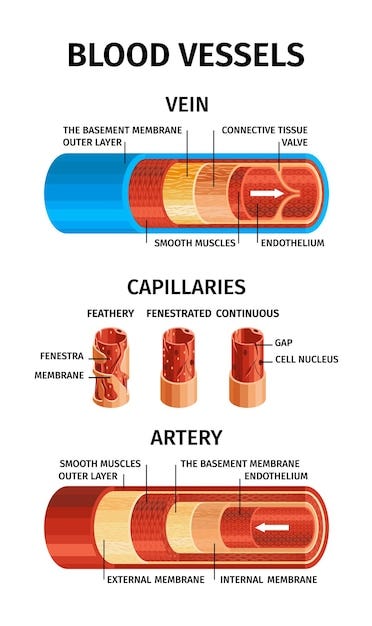
There are three main types of blood vessels:
Arteries:
blood vessels that transport oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
walls are thick, to withstand the high pressure of the blood moving within them
Veins:
carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart
walls are thinner compared to arteries
Capillaries:
smallest blood vessels
play a crucial role in exchanging oxygen and nutrients with the body's tissues while eliminating waste products
vessels are extremely thin and permeable to facilitate the exchange of substances between the blood and the tissues.
Basic Physiology
Circulation And the Heart, The Heart Is A Pump
The heart acts to pump the blood through distinct but interconnected circulatory systems called circuits (see above).
Note these key physiologic concepts related to the heart and its function
The heart is a pump:
blood is pumped to provide oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body
The heart is an organ
made of cells and tissues which require their own blood supply
The heart has a unique electrical conduction system
heart can independently generate/ transmit signals to
myocardium
this facilitates contraction and pumping of the blood
The cardiac cycle is a dynamic, rhythmic process involving the active pumping and circulation of blood.
Key term: cardiac cycle
interval beginning with atrial contraction, concludes with ventricular relaxation
Each heartbeat signifies a complete cycle in which the heart receives and ejects blood.
During diastole, the heart is in a relaxed state. This period allows the atria and ventricles to fill with blood. AV valves are open, facilitating movement of blood from the atria to the ventricles.
Systole is the phase in the cardiac cycle when the heart contracts. The AV valves forcefully shut and the ventricles push blood out to the lungs and the rest of the body through the (open) semilunar valves. When systole ends, the semilunar valves close in preparation for the next filling phase.
The Cardiovascular System & Health
It is important to remember that our cardiovascular system functions to deliver blood that will provide oxygen and nutrients to every cell in the body. Even the tiniest vessels, the capillaries, are crucial for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients in body tissues while eliminating waste products. Clinicians should be cognizant that heart disease remains the number one cause of mortality in the United States. Healthcare professionals must also be aware that patients with heart failure are at an increased risk for hospitalization.
This lesson article serves as a brief overview on the cardiovascular system, we invite you to view the optional videos that follow to learn more about the topic. In addition, Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions, Ch. 9 & 10, provides an in-depth learning experience on the heart, the circulatory system, and related terminology.
Recommended Reading (Optional)
Textbook
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions, Katherine Greene and Andrea Nelson
Read Chapters 9 & 10
Helpful Videos:
These videos will help provide you with a clearer understanding of the topics we introduced in the above lesson. Take your time reviewing the recommended reading and the videos. We will have a guided notebook and activity to help you review these materials over the next 2 weeks.
Browse our Notes section for more on the complementary lesson resources we provide.
The Cardiac Cycle, Animation
12 Lead ECG Explained, Animation
Echocardiogram Overview
Michigan Medicine
Anatomy of the Heart - External & Internal Structures
Resources:
CDC
FreePik.com
Michigan Medicine
NIH
Nelson, A., & Greene, K. (2021). Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions. University of West Florida Pressbooks. https://pressbooks.uwf.edu/medicalterminology/
Unsplash