CQRG 2024 Medical Terminology Bootcamp
SESSION 8 / INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
Welcome!
If you are new to our medical terminology program we invite you to browse our previous lessons and program activities. Simply click on the PROGRAMS tab above to view individual lessons and materials. Additional activities and reviews are posted on a weekly basis in the NOTES section. Each lesson in the program is a standalone experience, so there is never a worry if you need to take a break. Subscribe to receive the lessons emailed to you, or follow along in the Notes section.
The Nervous System
The fundamental component of the nervous system is the neuron.
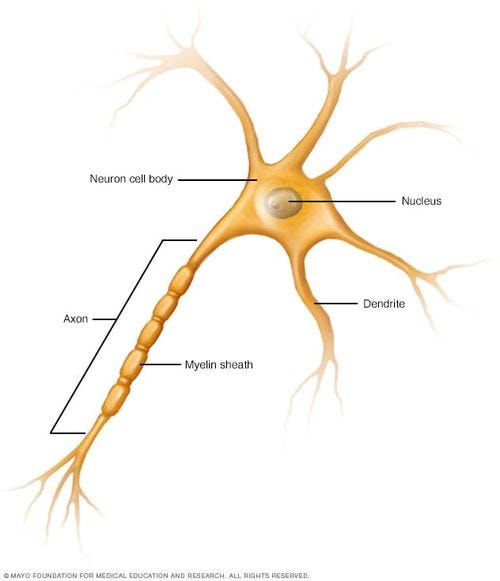
The neuron (nerve cell) is the basic unit of the nervous system. Transmission of signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs, is facilitated by the nervous system. Through its activity, the nervous system governs various functions such as movement, respiration, vision, cognition, and more.
Basic Anatomy
Our nervous system is divided into the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system comprises nerves that extend from the spinal cord to various parts of the body.
A neuron is composed of a cell body (soma), including a cell nucleus, and extensions called axons and dendrites. The axons and dendrites allow neurons to communicate.
Glial cells are a type of cell that support neurons and their activities.
Glial Cells
The medical term glia comes from the Greek word meaning, “glue.”
Glial cells are thought of as supporting cells. There are 6 kinds. These specialized cells function to assist neurons complete activities focused on communication.
Four types of glial cells are found in the central nervous system and two are found in the peripheral nervous system.
Glial Cells of the Central Nervous System
Astrocyte
Oligodendrocyte
Microglia
Ependymal cell
Glial Cells of the Peripheral Nervous System
Satellite cell
Schwann cell
Myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich substance surrounding nerve cell axons.
Myelin membranes are formed by, and part of Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system and oligodendroglial cells in the central nervous system. Each cell that generates myelin covers only one segment of an axon. The nodes of Ranvier, which are interruptions in the myelin sheath along the axon, are essential for propagation of action potentials.
The myelin sheath is a protective layer surrounding nerve cells in the central nervous system. In multiple sclerosis (MS), the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the myelin sheath, disrupting nerve communication and causing various neurological symptoms. This damage to the myelin sheath is a hallmark of MS.
Physiology
One of the primary functions of the nervous system is to receive information (sensation) about the environment (internal &/or external).
The nervous system plays a crucial role in gathering information from surroundings and producing appropriate reactions to that information (motor responses). It can be categorized into regions that handle sensation (sensory functions) and response (motor functions), but there is an additional function that must not be overlooked. Sensory input must be integrated with other information, this might include memories, emotional state, and learning (cognition).
Certain areas of the nervous system are referred to as integration or association areas. The process of integration merges sensory perceptions with higher cognitive functions.
Control
The somatic nervous system (SNS) is accountable for the conscious perception and voluntary motor responses. Voluntary motor response refers to the contraction of skeletal muscle, however these contractions are not always intentional in the sense that one must have the desire to execute them. Certain somatic motor responses are reflexes and frequently occur without a conscious intention to carry them out.
Recommended Reading (Optional)
Textbook
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions, Katherine Greene and Andrea Nelson
Read Chapter 8
Helpful Videos:
Structure function and types of neurons | Human Anatomy | 3D Biology
What happens during an MRI examination?
Multiple Sclerosis MRI
Don’t Forget The Nervous System Lesson Supplement:
https://www.flipbookpdf.net/web/site/094e80fbc9eb909ad782ee775232d4953ef009d8202404.pdf.html#page/1
Bootcamp Lesson Resources:
Elearnin (Youtube Video)
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professions,
Katherine Greene and Andrea Nelson
NIH
Siemens (Youtube Video)
Unsplash